Promoting the open and accountable management of oil, gas and mineral resources
EITI Global
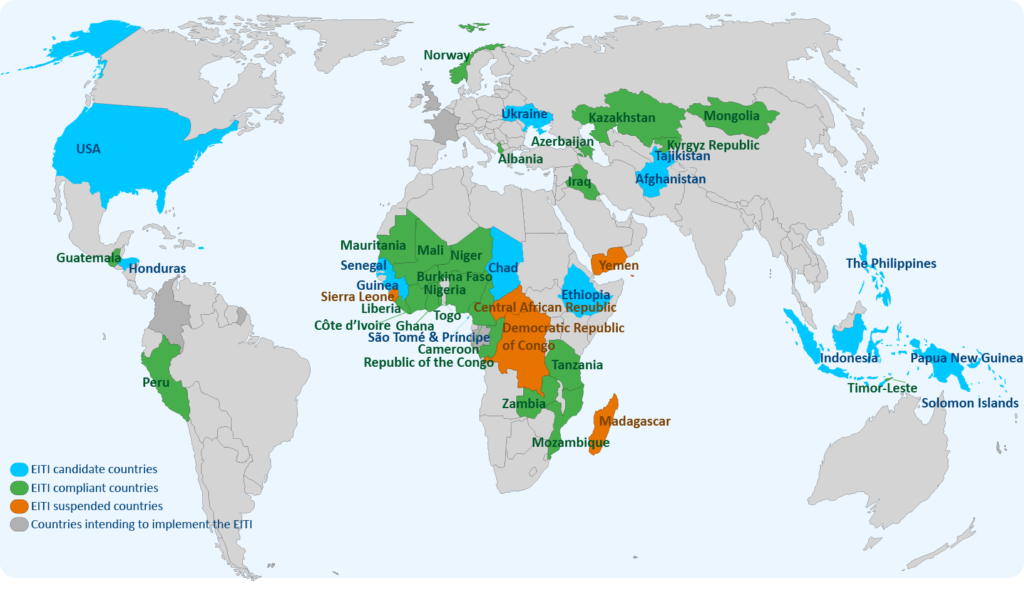
Headquartered in Oslo, Norway, the International Secretariat is a small team with origins from all corners of the globe. The International Secretariat is responsible for the functioning of the EITI Association and supports more than 50 countries in implementing the EITI Standard. EITI work spans across different areas such as country support, policy, communications, data analysis and administration.
The culture is underpinned by values of integrity, professionalism and respect for diversity. With over 25 countries represented, EITI value differences in backgrounds, culture, perspectives and languages. EITI believe those differences are an important part of what drives innovation and progress in EITI.